Five Forces Model
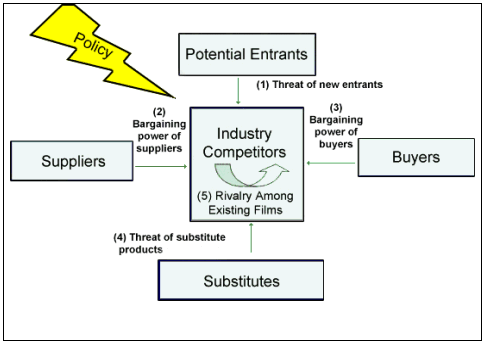
The Five Forces Model (developed by Dr. Michael Porter of Harvard University) serves as a framework for examining competition that transcends industries, particular technologies, or management approaches. The underlying fundamentals of competition go beyond the specific ways individual companies go about competing (i.e. Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats (SWOT) analysis; the 4P's of marketing: product, price, place, promotion). The underpinning of this framework is the analysis of the five competitive forces acting upon an industry and their strategic implications (Fig. 2)
The Five Forces Model looks at five areas of competition in the marketplace:
- Threat of new entrants (Barriers to entry)
- Bargaining power of suppliers
- Bargaining power of buyers
- Threat of substitute products or services
- Rivalry among existing firms
In addition to the five forces, a sixth force, governmental policies is added to Porter's model because of its influence on all the other forces.
By understanding the competitive forces within the redcedar industry, participants in the market can develop successful strategies to influence the forces for their own benefit.
|
| Figure 2: Forces driving industry competition |

